The Creditsafe Payment Analysis Report is a quarterly publication that gives you key insights into how well businesses are paying their bills both across the country and in different industry sectors. The report will help you understand key industry trends, while also allowing you to benchmark your company’s financial health against other businesses in your industry. The report will also provide useful context to help you determine the risk levels associated with doing business with customers – and set the best credit terms to keep your cash flow healthy and grow your business long-term.
Our data comes from over 9,000 trusted and official sources and is updated up to 5 million times a day to include credit scores and limits, financial information on up to three years of annual accounts, bankruptcies, judgments and lawsuits. We also have a reputable track record of predicting up to 70% of business failures 12 months in advance. The Creditsafe Trade Payment database now holds more than $10 trillion of information in value terms based on over 320 million payment experiences.
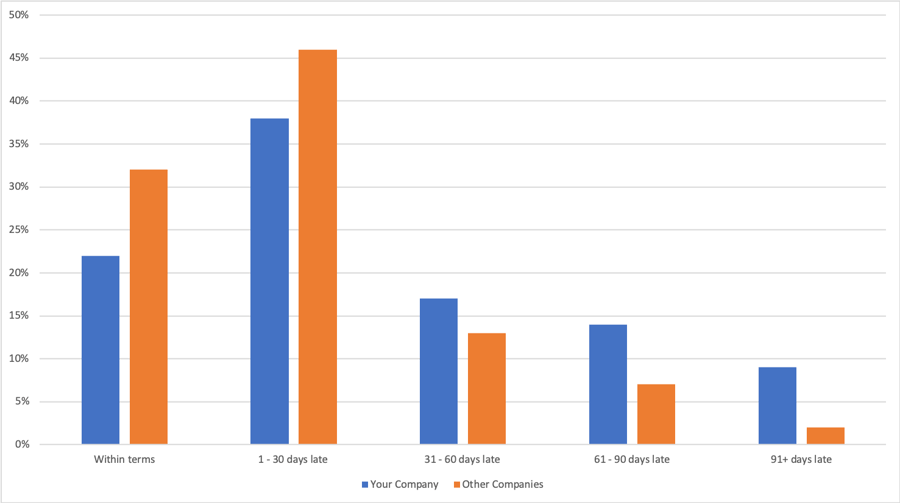
The data is based on a Days Beyond Terms (or DBT) score derived by Creditsafe for each business across the country, which is aggregated by industry to provide a key indicator of how well companies pay their bills. As a rule of thumb, a lower DBT score indicates that a company is a more reliable payer. The report breaks down this information across all key industry sectors based on their two-digit NAICS code.
Creditsafe’s team use the latest analytics tools and methodologies to convert this raw data into a true DBT score. This process ensures that the score is significantly more responsive than a simple average as it gives greater significance to payments that are severely delinquent or have relatively large dollar values. In effect, the larger and later a payment is, the greater detrimental impact it will have on the overall DBT. You should also be aware that a full DBT score may change once an unpaid invoice is more than 91 days beyond terms, meaning that a full quarter’s DBT may be adjusted once all outstanding invoices are settled or fully aged.